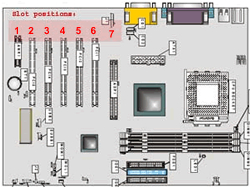
To understand better how to decide which risercard to use it is convenient to know about the way slots are numbered. On the picture you can see how the slots are numbered. A lot of mainboards don't have any slot at all at position
7, in that case the AGP slot (if available) will be on position
6. The risercard in your system is always mounted at position
6. So the first step is to decide what kind of slot the risercard needs to have on position
6, PCI (32-bit, 64-bit, PCI-express) or AGP. When using a 2U risercard , the risercard also needs to be connected to two other slots for supporting all three slots on the risercard . Usually a 2U risercard uses slot 1(AGP), 2(PCI) and 3(PCI) or slots 2(AGP/PCI), 3(PCI) and 4(PCI). There are also some special risercards which can support other slots, those are mostly flatcable-risercards . An example of this is a risercard that supports slots
2,
3 and
6.
DD-603605-C7
Drives:
Dimension(WxHxD):
• 0.00 x 0.00 x 0.00 inches
• 0.0 x 0.0 x 0.0 mm
DD-611
Drives:
Dimension(WxHxD):
• 0.00 x 0.00 x 0.00 inches
• 0.0 x 0.0 x 0.0 mm
DD-611-CX
Drives:
Dimension(WxHxD):
• 0.00 x 0.00 x 0.00 inches
• 0.0 x 0.0 x 0.0 mm
DD-630660-C7
Drives:
Dimension(WxHxD):
• 0.00 x 0.00 x 0.00 inches
• 0.0 x 0.0 x 0.0 mm
DD-631-CX
Drives:
Dimension(WxHxD):
• 0.00 x 0.00 x 0.00 inches
• 0.0 x 0.0 x 0.0 mm
DD-632661-C9
Drives:
Dimension(WxHxD):
• 0.00 x 0.00 x 0.00 inches
• 0.0 x 0.0 x 0.0 mm